Applications
 Part of the Oxford Instruments Group
Part of the Oxford Instruments Group
Expand
Collapse
By Ray Spits, Collaborations Programme Manager
One of the UK’s National Quantum Strategy Missions is demonstrating large-scale error correction capabilities with a billion quantum operations, specifically for accelerated drug discovery. While this sounds like a momentous task, one initiative working to help make it a reality is Innovate UK-funded QuPharma.
QuPharma is a project led by digital quantum computing company SEEQC, with partners including Oxford Instruments NanoScience, and world-leading pharmaceutical developers Merck KGaA. The aim of the initiative is to accelerate the scale-up and implementation of quantum technologies in drug discovery. The project began in March 2022 and is now in its seventh quarter.
The project was awarded an additional £5m grant by Innovate UK to help achieve its goal. We spoke to Ray Spits, Collaborations Programme Manager at Oxford Instruments NanoScience, about our collaboration with SEEQC, and how projects like this are helping to drive the industry forward.
Can you explain the QuPharma project with SEEQC? What is its goal?
In short, the goal of the QuPharma project is to deliver a scalable, full stack quantum computing platform with commercial access for the pharmaceutical industry. More specifically, the project has three core aims:
Build a quantum computing platform that demonstrates a clear pathway to solving computational problems that will reduce the cost and time of drug discovery.
Lead adoption of quantum computing by identifying use cases and demonstrating system performance, encouraging investment and involvement from pharmaceutical companies in the UK.
Build a platform where all components, hardware and software, can scale up to the qubit count and quality necessary for quantum advantage in pharmaceutical applications.
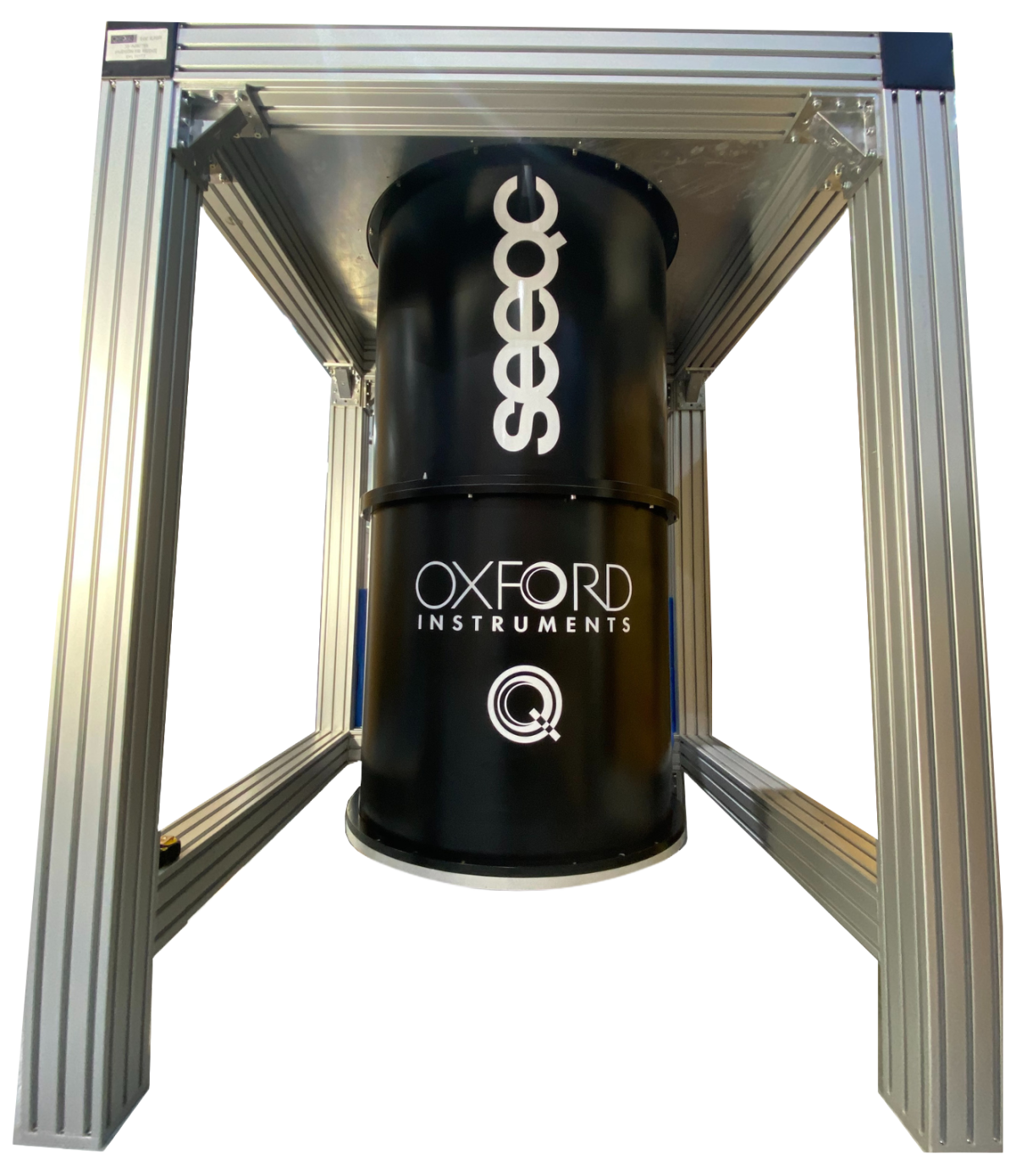

What is Oxford Instruments NanoScience’s role in the QuPharma project?
Our role in the project is twofold. With our experience in cryogenic systems, we have a consultative as well as a technical role, providing SEEQC with our Triton XLQ dilution refrigerator, which is a precursor to our world-leading Proteox platform. Whilst the XLQ uses exactly the same main dilution refrigerator insert as our Proteox platform, a hybrid arrangement of line-of-sight wiring solutions are used as well as the Secondary Insert concept adopted by the Proteox platform. We have designed and manufactured custom Secondary Inserts of this XLQ to optimally support SEEQC’s fully integrated digital chip-based quantum computer architecture. SEEQC is using this system to enable the cryogenic environment needed for its superconducting quantum computing platform. In the future, we will also provide custom wiring solutions to support SEEQC's proprietary Single Flux Quantum control technology and take full advantage of the ultra-low latency, fast readout and co-processing enabled by this technology.
Who are the other partners involved and what are their roles?
Achieving a project of this scale requires cross-industry collaboration and the open exchange of expertise and experience - missions like this are never achieved in isolation! Alongside SEEQC, we worked with a consortium of business and research partners including Merck KGaA, Riverlane, the National Quantum Computing Centre (NQCC), STFC Laboratories, the University of Oxford, and the Medicines Discovery Catapult (MDC,.
As leaders of the project, SEEQC has designed, built, and benchmarked a full-stack quantum computer incorporating their integrated chip based quantum architecture - the first of its kind - improving system latency, stability, performance and decreasing costs. Merck’s role in the project is a commercial use-case provider and platform validator. The team’s feedback has allowed us to prioritise features of software and set specifications on hardware quality.
We spoke with Matthew Hutchings, Chief Product Officer at SEEQC about his experience as part of the QuPharma project. “Leading QuPharma has been an incredible experience for us. It has shown how important collaboration is when it comes to advancing the commercialisation and practical applications of quantum computing. From industry, to academia, to government - completing such a project means bringing together expertise and experience from all corners of the ecosystem. It’s been a privilege to lead a project that is advancing the tangible and genuinely impactful applications of quantum computing.”
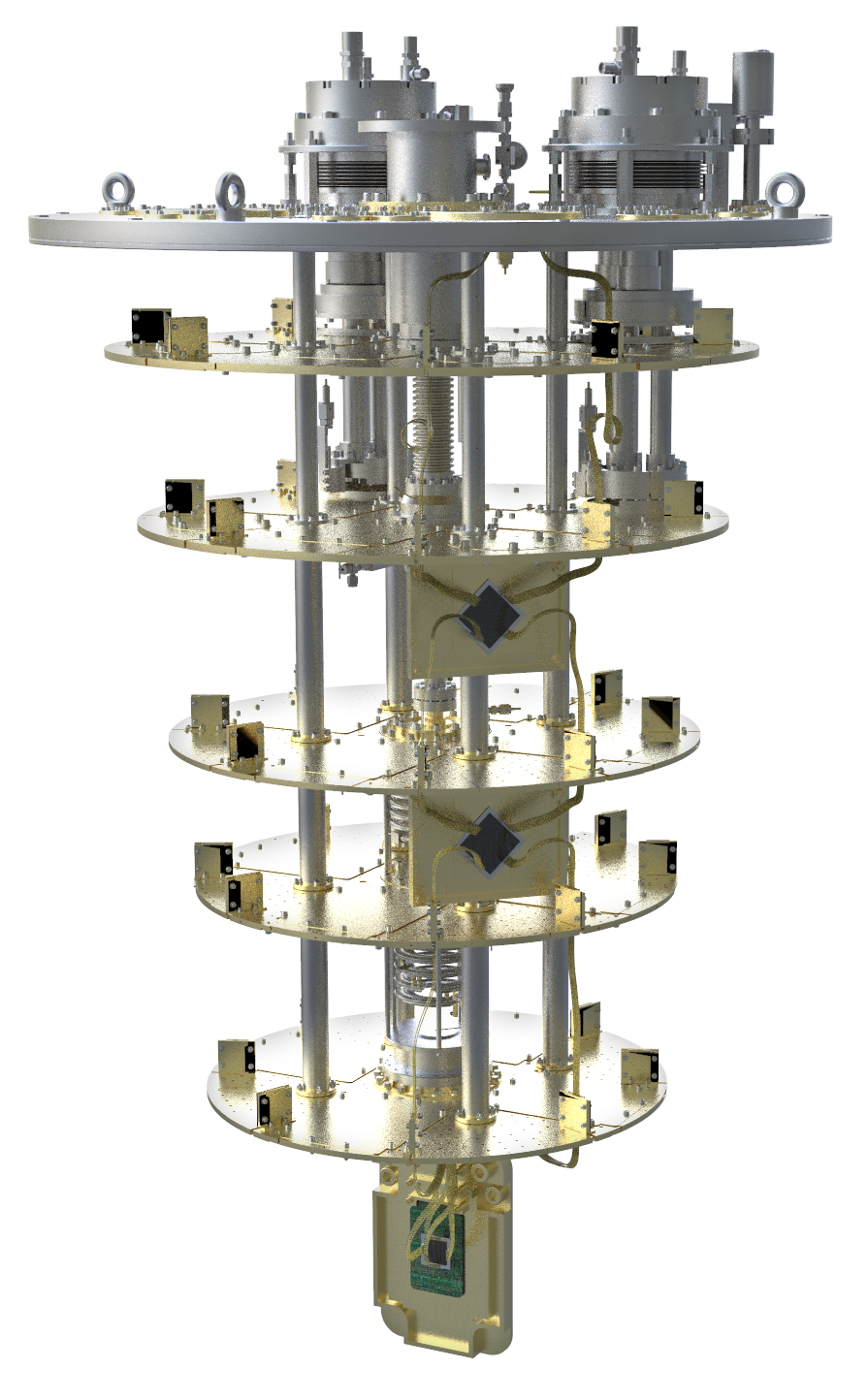
Have Oxford Instruments NanoScience and SEEQC collaborated in the past?
Yes, NanoScience has a recent history of collaboration with SEEQC. In 2020, we partnered with them as part of a larger consortium for another Innovate UK project focused on establishing R&D centres and foundries in the UK. The goal of this project was to provide businesses with facilities and expertise for developing and manufacturing superconducting quantum circuits. For the project, we provided two ProteoxMX systems equipped with Secondary Inserts, external electronic measurement equipment, and the direct support of an expert measurement scientist. SEEQC contributed its extensive experience in chip fabrication to support the project’s goal of establishing a UK based quantum foundry service.
How has this project contributed to the scale-up of quantum technologies? What are the implications for pharmaceuticals?
The QuPharma project aims to build enterprise-level quantum computers for pharmaceutical R&D. The SEEQC platform achieves this by eliminating key technical bottlenecks to scaling quantum computers. With the project’s success, quantum advantage is one step closer for simulating photodynamic drugs, a method that scales exponentially even with today's supercomputers. Its performance and potential can therefore be massively optimised using quantum technologies. The prototype platform being developed in the QuPharma project is intended to clearly demonstrate a path to commercial scale-up of such a quantum computer for advanced pharmaceutical innovation and development.